How to split A Large File into Smaller Parts in Linux
You can split a large file into smaller parts in Linux using the split command.

When working on real project environments, ther are scenarios where you end up having a large files. For example log files, Large Datasets etc.
You can split a large file into smaller parts in Linux using the split command.
The split command is like a big scissors for cutting large files into smaller files. It helps when you have a huge file and want to break it down into smaller chunks that are easier to manage or share.
Let's see how we can use this command to make our lives easier.
Split the File Based on Lines
Let's say you have a massive log file named log.txt that has a lot of lines to handle efficiently. To break it into smaller chunks based on lines run the below command:
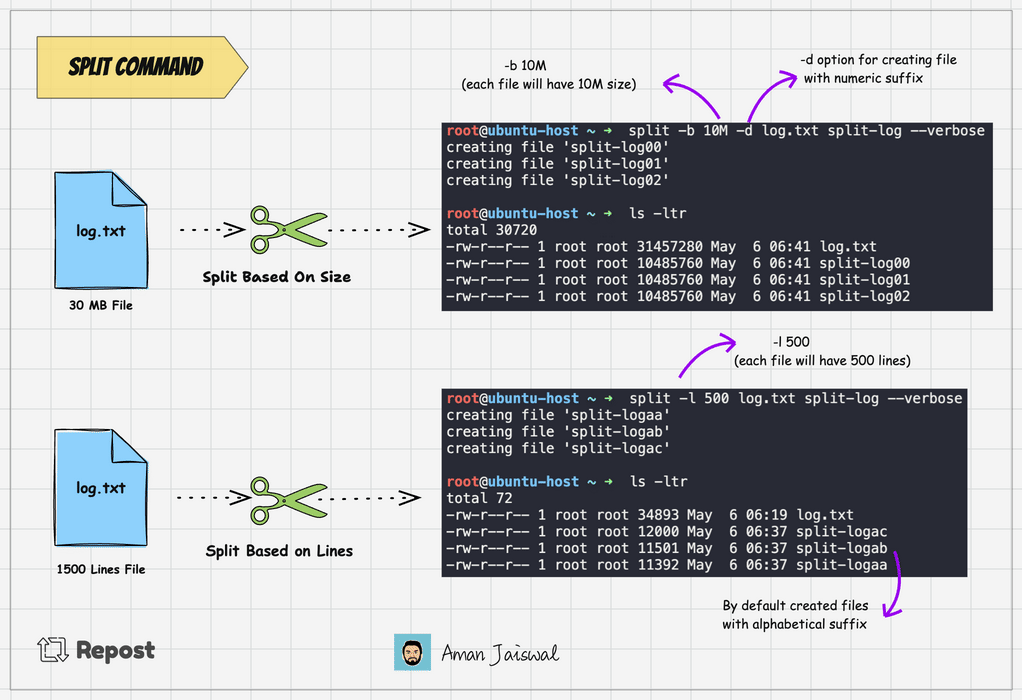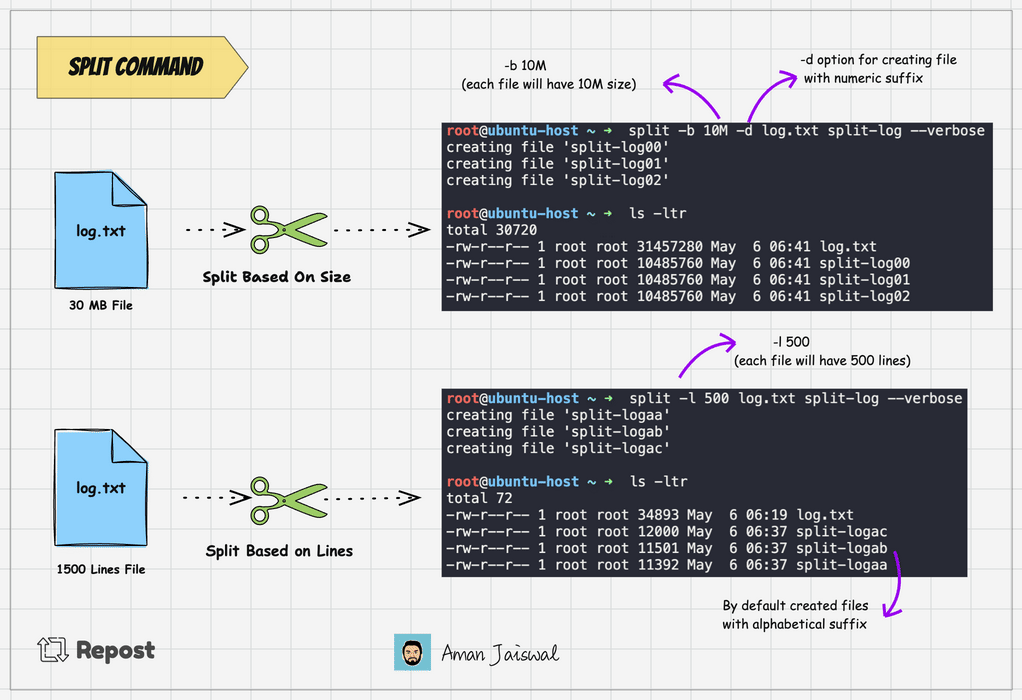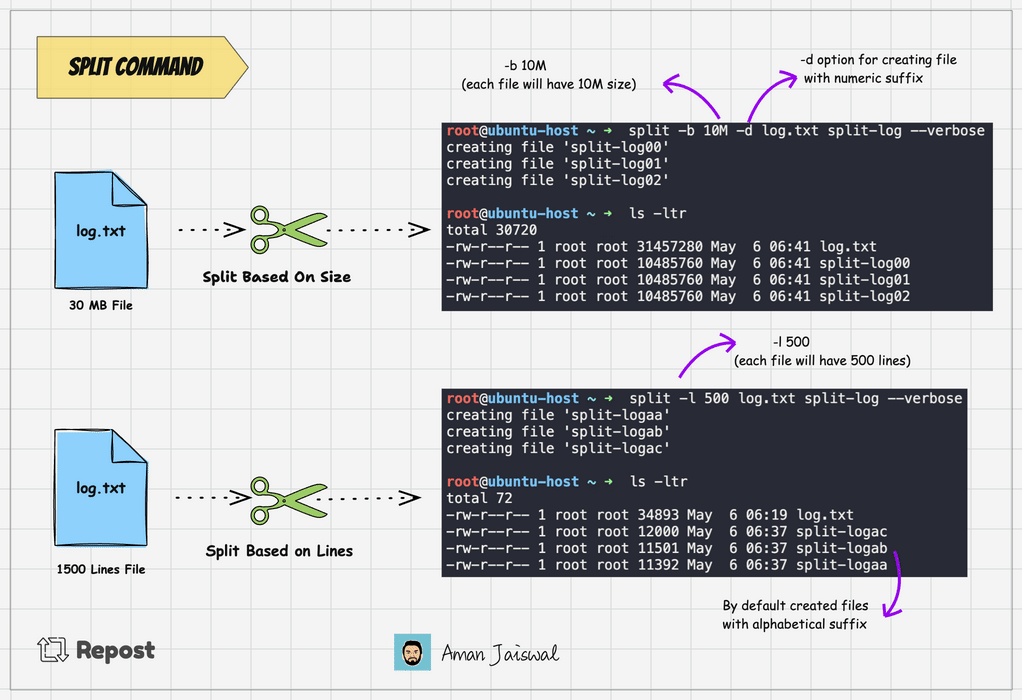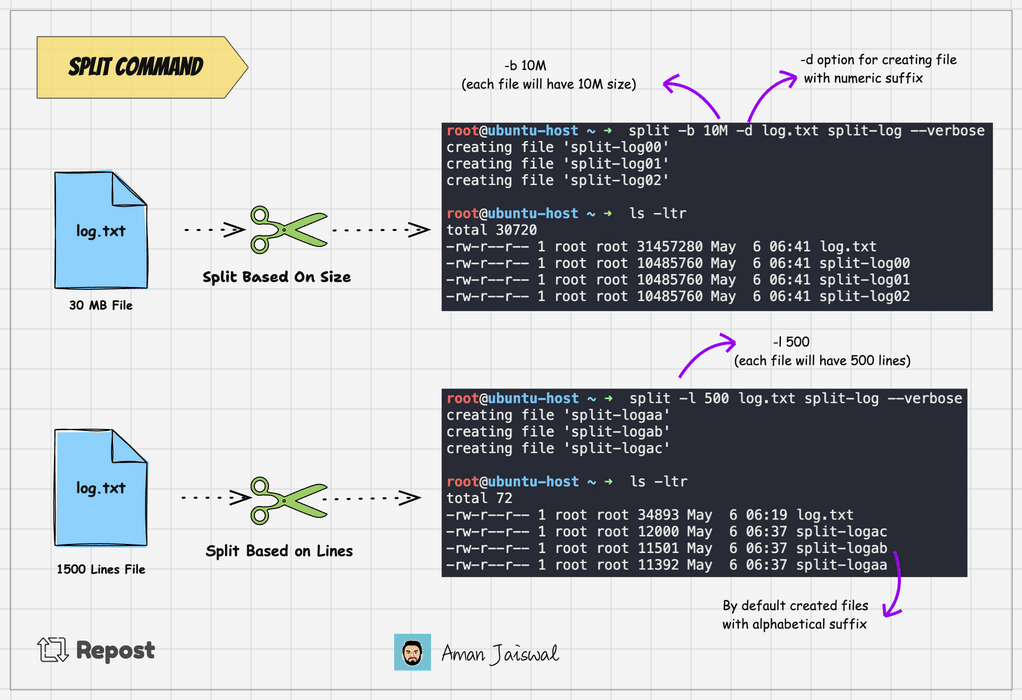
split -l 1000 log.txt split-logThis command will split the log.txt file into multiple files, each containing 1000 lines, with names like split-logaa, split-logab, split-logac and so on.
Split command adds the alphabetical suffix to the prefix for new files. It's the by default behavior. To add the numeric suffix, we can use the -d option.
split -l 1000 -d log.txt split-logThe above command will create the file like split-log00, split-log01, split-log02, and so on.
Split the File Based on Size
We can split the file based on byte size as well. Suppose you have a file that is 100MB in size, you can use the -b option to break it into smaller chunks.
split -b 25M -d log.txt split-logThe above command will divide the log.txt file into 4 files, each 25MB.
To check the output of the command, we can use the --verbose option. It will show the files created on the terminal.
Split the File equally into Small Files
If we want to split a file into n equal chunks then we can use the -n option.
split -n 2 log.txt split-logThe above command will create 2 equal-length files split-logaa and split-logab
Isn't that amazing?
The split command is a lifesaver when dealing with large files, whether you're processing log data, backing up important files, or preparing data for parallel processing.
Real World Examples
Assume we have a file called error.log. It's a very lengthy file so we want to divide it into chunks so that we can analyze it easily.
We want it to divide so that each file has around 800 lines.
➜ split -l 800 -d error.log error-chunk- --verbose
creating file 'error-chunk-00'
creating file 'error-chunk-01'
creating file 'error-chunk-02'
creating file 'error-chunk-03'
creating file 'error-chunk-04'
➜ ls -ltr
total 172
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 82893 May 6 11:08 error.log
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7200 May 6 11:09 error-chunk-04
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19200 May 6 11:09 error-chunk-03
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19200 May 6 11:09 error-chunk-02
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 19001 May 6 11:09 error-chunk-01
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18292 May 6 11:09 error-chunk-00
We can see that the split command divided the error.log file into files different files each having 800 lines.
Also, in Large Data Processing workloads, when working with extremely large files that cannot fit into memory, splitting them into smaller chunks allows for parallel processing or analysis, improving performance.
Splitting large files into smaller parts can facilitate easier and faster transfer over networks or storage devices with size limitations or slower speeds.
Reassembling the File
After splitting a file into smaller parts, you can reassemble the file by concatenating the split files back together in the correct order. The process of splitting and reassembling a file does not inherently cause problems with file integrity, as long as the splitting and concatenation are done correctly.
To merge the split files back into the original file, you can use the cat command followed by the split file names in the correct order. For example:
cat file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt > original_file.txtPerformance Implications Using split command
Running the split command on large files can have some performance implications.
Splitting a large file involves reading the entire file from disk and writing the split parts back to disk.The performance of the split command is influenced by the disk I/O speed of the system.
If the file is large and the disk I/O is slow, the splitting process may take a considerable amount of time.
To minimize the performance impact when splitting large files:
- Ensure sufficient disk space is available for the split files.
- Choose an appropriate split size based on your requirements and the file size.
split command Alternatives
There are several alternatives to the split command that you can use to split large files into smaller parts. Here are a few options:
csplitcommand:csplitis a utility that allows you to split a file based on context-based patterns or line numbers.sedcommand:sedis a stream editor that can be used to split files based on line numbers. It allows you to specify the range of lines to extract into separate files.- Using scripting languages like python: You can write custom scripts in Python or other programming languages to split files based on your specific requirements. This is particularly useful in Data engineering tasks.